|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
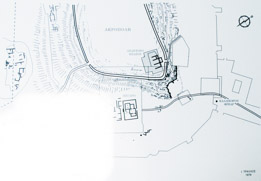
| Early Classical period At the beginning of the C 5th BC work began to create a temple twice the size of its predecessor but was interrupted by the Persian wars. | ||
|
|
|
|

|
||
|
|
|
|
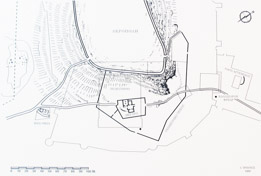
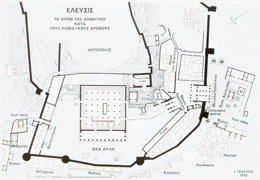
| Reconstruction of Sanctuary during the Archaic period - Peisistratos time. | ||
|
|
|
|

|
||
|
|
|
|
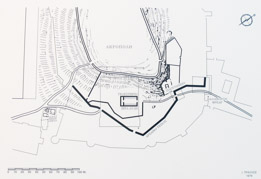
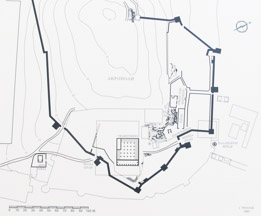
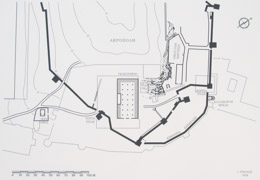
| Reconstruction of Santuary during the Roman period. | ||
|
|
|
|

|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
||
|
|
|
|
| C7thBC burial amphora from Western Cemetery. Proto-Attic style ... | ||
|
|
|
|

|
||
|
|
|
|
| ... with neck depiction: the blinding of Polyphemus by Odysseus and his companions - body depiction: Perseus beheading the Medusa. | ||
|
|
|
|

|
||
|
|
|
|
| Large amphoras were used in burials: some cinerary urns contained cremated bodies, other pot burials contained infants or small children. | ||
|
|
|
|

|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
||
|
|
|
|
| C6thBC part of a loutrophoros depicting a procession of bearded men: three musicians holding kithara and flute, three holding myrtle leaves and the seven a tripod. | ||
The photographs on this site are for the use of the Participants of the Event and their Families and Friends and may be copied and printed for personal use only. Their use for commercial purposes is governed by copyright and permission must be obtained from the webmaster . Events-On-Line ~ (C) 2013